The Bitcoin Lightning Network is a groundbreaking second-layer protocol built on top of Bitcoin’s main blockchain. It was created to tackle Bitcoin’s biggest challenges: slow transactions and high fees. By moving payments off-chain through secure payment channels, the Lightning Network enables near-instant, ultra-low-cost BTC transfers. This makes micro-payments and everyday spending practical. Because of this, Lightning is called a Layer 2 scaling solution , it preserves Bitcoin’s security and decentralization, while making it faster and cheaper for everyone.
Klever Wallet now supports BTC deposits through three powerful networks, giving users flexibility based on speed, fees, and use case:
- Bitcoin Lightning Network
- Liquid BTC (Sidechain)
- Bitcoin Main Chain (Mainnet)
Below is a complete guide on how each one works, why they differ, and how to use them.
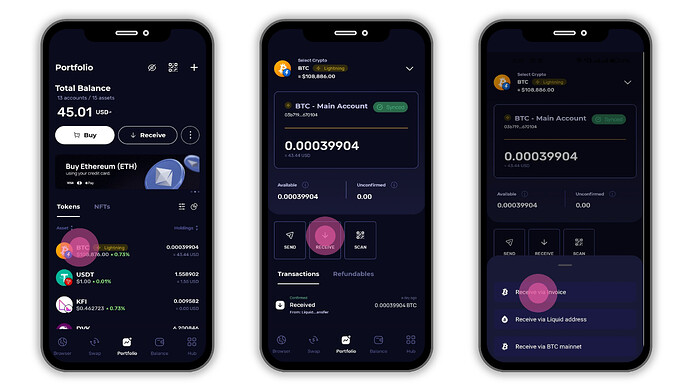
1. Deposit BTC via the Bitcoin Lightning Network
What it is:
The Lightning Network uses invoices or QR codes instead of a permanent wallet address. Each invoice is a unique, one-time payment request that routes funds instantly through payment channels off-chain.
Why no address:
Because Lightning relies on temporary channels and dynamic routing, it does not use a static receiving address like Bitcoin Mainnet , instead, you generate a new invoice for each payment.
How to deposit:
- Open your Klever Wallet on Android or iOS.
- Tap on Receive and choose Bitcoin (BTC).
- You will see three network options: Lightning, Liquid, and Bitcoin Mainnet.
- Select Lightning Network.
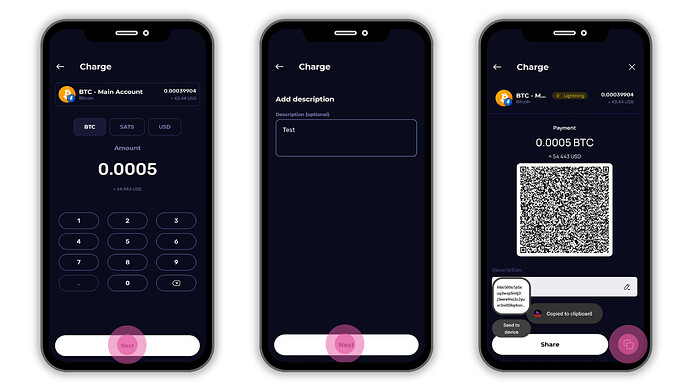
- Under Charge, choose your preferred currency (e.g., USD) and enter the amount you wish to deposit (for example, 20 USD, which converts to BTC automatically).
- Click on Create Invoice. Note: You must enter an amount ,you cannot create an open invoice without it.
- The wallet generates a unique Lightning invoice and QR code.
- Click on Copy Invoice Number to copy the invoice.
- Paste this invoice into the payment field on the platform you’re withdrawing BTC from.
- Important : The invoice is valid for 12 hrs,the payment must be completed before it expires.
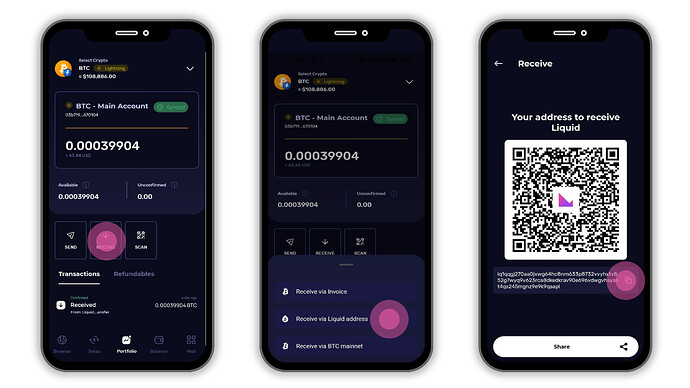
2. Deposit BTC via the Liquid Network
What it is:
Liquid BTC (L-BTC) is Bitcoin pegged 1:1 on the Liquid sidechain, designed for faster transactions and confidential trading. Unlike Lightning, Liquid has a reusable wallet address, just like Bitcoin mainnet.
How to deposit:
- In the same Receive screen, select the Liquid Network.
- Klever Wallet will display your unique Liquid BTC address (starting with
VT...orEx...). - Copy this address and paste it into the withdrawal field on any exchange or wallet that supports L-BTC.
- Complete the withdrawal, your funds will arrive in your Klever Wallet once the Liquid transaction is confirmed (typically 1–2 minutes).
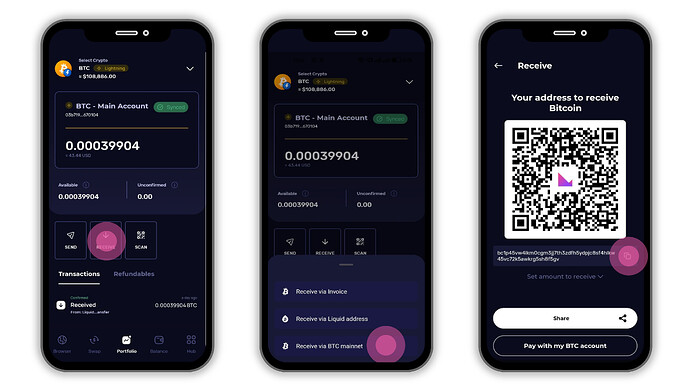
3. Deposit BTC via the Bitcoin Main Chain
What it is:
Bitcoin’s main chain is the original blockchain network where all transactions are permanently recorded on a public ledger. It uses standard wallet addresses that can be reused at any time to receive BTC.
How to deposit:
- In the Receive screen, choose Bitcoin Mainnet.
- Klever Wallet will show your standard BTC address (starting with
bc1,3, or1). - Copy this address and paste it into the withdrawal field on the sending platform.
- Confirm the transaction ,your BTC will appear in your wallet once the Bitcoin network confirms it (typically 10–60 minutes, depending on network traffic and fees).
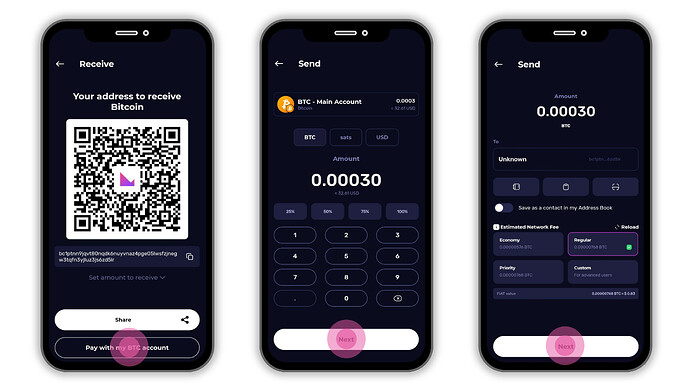
-
Tap on Pay with my BTC account , enter the amount you want to send.
-
Choose your network fee:
- Economy (slowest, cheapest)
- Regular (balanced)
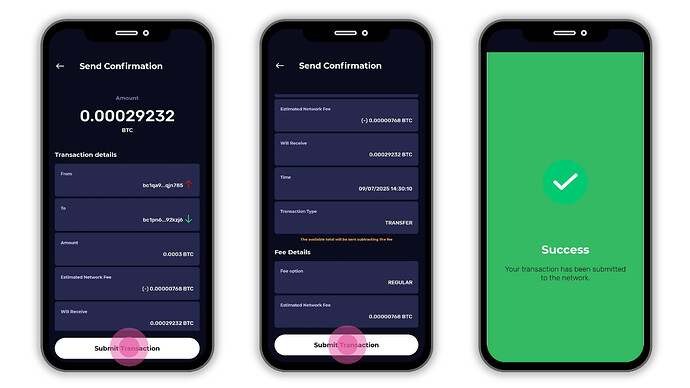
- Priority (fastest)7. Review the amount, recipient, and fees.8. Tap on Submit Transaction and You’ll see a Success screen once the transaction is submitted to the Bitcoin network.
How These Networks Compare
Here’s a simple table to help you understand the main differences:
| Bitcoin Mainnet | Lightning Network | Liquid BTC (Sidechain) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Address | Static (e.g. bc1...) |
Dynamic (invoice like lnbc...) |
Static (starts with VT... or Ex...) |
| Expiry | None | Usually expires | None |
| Reusable | Yes | No | Yes |
| Explorer | On-chain (Mempool, Blockstream) | Not directly on-chain (uses node explorers like 1ML) | Liquid block explorer (e.g., Blockstream.info/liquid) |
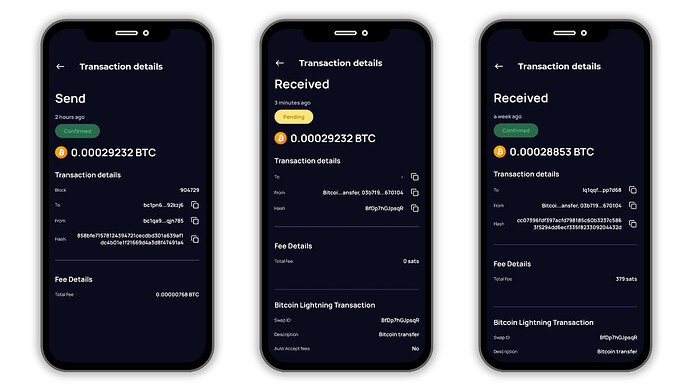
How Swaps Connect On-Chain BTC to Lightning (and Vice Versa)
When you move BTC between different networks , for example, sending Bitcoin Mainnet BTC to a Lightning wallet , you’re not sending funds directly into a Lightning channel. Instead, this process uses a smart mechanism called a Submarine Swap (also called a swap-in).
Here’s how it works, step by step:
- The Lightning wallet (or the swap service behind it, like Breez SDK) provides you with a regular on-chain BTC address.
- You send BTC to this on-chain address, just like any other Bitcoin transaction.
- Once the on-chain transaction is confirmed, the system detects it automatically.
- A Submarine Swap is then performed in the background, your on-chain BTC is swapped for BTC that lives inside the Lightning Network.
- The equivalent amount is credited to your Lightning balance, and you can now spend it instantly via Lightning invoices.
So, while it looks like you’re sending on-chain BTC directly “into” Lightning, technically you’re sending it to a swap provider that manages the channel opening and liquidity for you.
The same concept works the other way around too:
- When you want to withdraw BTC from Lightning back to on-chain (a swap-out), the service closes the channel or routes funds through a swap provider.
- The Lightning BTC is exchanged for on-chain BTC, and you receive it at your regular Bitcoin address.
Why This Matters
- Lightning is perfect for instant, low-cost payments , ideal for everyday transactions or small amounts.
- Liquid is great for faster and more private transfers between exchanges, traders, and institutional users.
- Bitcoin Mainnet is the classic, fully decentralized option for storing and transferring BTC securely on the public blockchain.
With Klever Wallet, you get the freedom to choose the best network for your needs ,whether you want speed, privacy, or the security of Bitcoin’s base layer.